The Crucial Role of Debt Finance in India’s Economic Landscape
Introduction:
In the pulsating heart of India’s economic engine, debt finance plays a pivotal role in steering the nation towards progress. As we delve into the intricacies of this financial mechanism, we unravel the web of opportunities and challenges it presents in the dynamic tapestry of India’s economic landscape.
Table of Contents
Fueling Growth:
Debt finance, in its essence, acts as the lifeblood of businesses and governments alike. It’s the financial catalyst that propels infrastructural development, technological advancements, and social welfare programs. In a country as diverse and vast as India, the infusion of debt capital becomes instrumental in addressing the growing needs of a burgeoning population and a rapidly evolving economy.
Infrastructure Development:
One of the most tangible impacts of debt finance in India is witnessed in the construction of critical infrastructure projects. From highways that connect remote villages to urban centers to the development of modern airports and ports, debt becomes the cornerstone for financing these colossal undertakings. The ability to borrow funds empowers the government to bridge the infrastructure gap and provide citizens with better connectivity and accessibility.
Entrepreneurial Ventures:
On the flip side, debt financing isn’t solely the realm of governments; it’s the lifeblood of entrepreneurship. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) often rely on loans to kickstart or expand their businesses. Whether it’s procuring machinery, expanding production capacity, or investing in research and development, debt finance becomes the fuel that propels the entrepreneurial spirit, fostering economic diversity and innovation.
Job Creation:
A ripple effect of debt-financed entrepreneurial ventures is the creation of employment opportunities. As businesses grow, so does the demand for skilled labor. This not only addresses the unemployment challenges in the country but also contributes to the overall economic prosperity by fostering a more productive and engaged workforce.
Education and Healthcare:
Debt finance isn’t just about constructing concrete structures; it also has a softer side that directly impacts the quality of life for citizens. Investments in education and healthcare are often funded through debt instruments. Improved schools, better-equipped hospitals, and advanced medical research facilities become a reality when financial resources are mobilized through debt financing.
Challenges and Prudent Management:
While debt finance serves as a powerful tool for progress, it comes with its own set of challenges. One of the foremost concerns is the burden of debt repayment. Striking a balance between leveraging debt for development and ensuring sustainable repayment plans is a delicate dance for policymakers. Prudent debt management becomes crucial to prevent the accumulation of an unsustainable debt burden that could impede future economic growth.
Global Economic Dynamics:
India’s reliance on debt finance is also intertwined with global economic dynamics. Fluctuations in interest rates, global market conditions, and the country’s credit rating can significantly impact the cost and availability of debt. A delicate balance must be maintained to ensure that debt remains a facilitator of growth rather than a hindrance.
Conclusion:
In the grand tapestry of India’s economic journey, debt finance emerges as a powerful brushstroke that shapes the contours of progress. From towering skyscrapers to the rural hinterlands, debt finances the dreams and aspirations of a diverse nation. It is a tool that, when wielded judiciously, becomes the bridge between aspirations and achievements. As India continues its march towards becoming a global economic powerhouse, the role of debt finance will undoubtedly remain a central and evolving theme in its economic narrative.
Understanding Public Debt Challenges in India
In the intricate field of economic dynamics, public debt becomes a significant player, shaping the financial landscape of a nation. India, with its vibrant and diverse economy, is not exempt from the challenges that come with managing public debt. In this exploration, we unravel the intricacies, problems, and issues associated with public debt in the Indian context.
The Burden of Borrowing:
Public debt essentially represents the amount of money that a government owes to external creditors and domestic lenders. While borrowing is a common practice for governments to finance various projects and meet fiscal obligations, the challenge lies in managing the debt levels responsibly. In India, the burden of public debt has been a cause for concern, and finding the right balance is crucial for sustainable economic growth.
Budgetary Constraints:
One of the foremost issues stemming from high levels of public debt is the strain it puts on the government’s budget. A significant portion of the budget is allocated towards servicing the interest and repaying the principal amount of the debt. This leaves limited fiscal space for crucial sectors like healthcare, education, and infrastructure, hindering the government’s ability to address pressing socio-economic issues.
Interest Rate Volatility:
The specter of interest rate volatility looms large over public debt management in India. Fluctuations in interest rates can significantly impact the cost of servicing the debt. In a scenario where interest rates rise, the government may find itself grappling with higher interest payments, further squeezing the budget. Prudent measures to mitigate interest rate risks are vital for effective debt management.
Inflation Dynamics:
India’s economic landscape is marked by its susceptibility to inflationary pressures. Public debt, when not managed astutely, can exacerbate inflation dynamics. Excessive borrowing may lead to increased money supply, contributing to inflationary trends. Striking a balance between financing needs and inflation control becomes a delicate task for policymakers.
Currency Risk:
For a country with a diverse economic base like India, currency risk is an additional layer of complexity in public debt management. If a significant portion of the debt is denominated in foreign currencies, fluctuations in exchange rates can escalate the cost of repayment. This highlights the importance of a well-thought-out strategy to mitigate currency risks associated with public debt.
Crowding Out Private Investment:
High levels of public debt can potentially crowd out private investment. When the government absorbs a large share of available funds through borrowing, there’s less capital available for businesses and entrepreneurs. This can stifle private sector growth and innovation, hampering the overall economic vitality.
Fiscal Discipline and Reforms:
Addressing public debt challenges in India requires a multi-faceted approach. Fiscal discipline, prudent financial management, and structural reforms are imperative. Streamlining government expenditure, enhancing revenue generation, and implementing policies that foster economic growth are essential components of a comprehensive strategy to tackle public debt challenges.
Transparency and Accountability:
Transparent communication regarding the government’s borrowing activities is paramount. Ensuring accountability in the use of borrowed funds and the outcomes of public projects helps build trust among citizens. Moreover, involving stakeholders in the decision-making process fosters a sense of shared responsibility in managing public debt.
Conclusion:
Public debt, like the ebb and flow of tides, is an inherent part of a nation’s economic journey. In India, addressing the problems and issues associated with public debt requires a nuanced understanding of economic dynamics and a commitment to fiscal responsibility. As the nation navigates through these fiscal seas, the key lies in finding a delicate balance that ensures sustainable growth while safeguarding the welfare of its citizens. Through prudent management, transparency, and a commitment to reforms, India can chart a course towards a resilient and robust economic future.
Public Debt Management in India
Public debt management may sound like a complex financial jigsaw puzzle, but in the vibrant tapestry of India’s economic landscape, it’s a crucial piece that shapes the nation’s fiscal health. Let’s embark on a journey to demystify the world of public debt management, exploring how India tackles this intricate challenge.
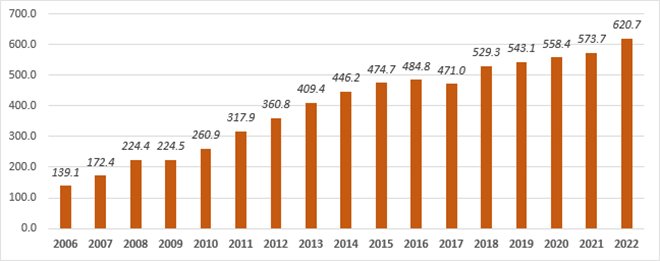
Understanding Public Debt:
At its core, public debt is the money a government borrows to fund various projects and meet its financial obligations. It’s like taking out a loan, but on a much grander scale. In a country as diverse as India, where ambitions soar high and development is a constant pursuit, public debt becomes a necessary tool to finance growth.
Striking the Right Balance:
The art of public debt management lies in striking the right balance. On one hand, borrowing is essential for funding infrastructure, education, and healthcare projects. On the other hand, excessive debt can pose risks to the economy, burdening future generations with repayment obligations. It’s a delicate dance between fueling growth and ensuring fiscal sustainability.
Diversifying Debt Instruments:
India’s approach to public debt management involves a diverse set of instruments. Government bonds, treasury bills, and securities are the tools in this financial toolbox. By diversifying these instruments, the government manages risks, attracts a range of investors, and maintains flexibility in meeting its financing needs.
Lengthening Maturities:
Imagine juggling debts with different due dates – it’s not an easy feat. To ease this financial juggling act, India focuses on lengthening the maturities of its debt. By extending the repayment period, the government aims to reduce short-term refinancing risks and create a more stable debt profile.
Market Borrowing and Strategic Planning:
Market borrowing is a key component of India’s public debt management strategy. The government engages with financial markets to raise funds through auctions of government securities. Strategic planning plays a pivotal role here – analyzing market conditions, assessing borrowing needs, and ensuring that the borrowing mix aligns with the broader economic goals.
Managing Interest Rate Risks:
Interest rates, like unpredictable weather patterns, can impact the cost of servicing debt. India’s public debt management strategy involves carefully navigating these interest rate risks. By employing a mix of fixed and floating-rate debt, the government aims to cushion itself against the turbulence of interest rate fluctuations.
Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Discipline:
Effective public debt management is intertwined with fiscal responsibility and disciplined budgeting. Ensuring that borrowed funds are allocated efficiently and contribute to long-term economic growth is paramount. The focus is not just on borrowing but on optimizing the utilization of funds for maximum impact.

Investor Confidence and Transparency:
Maintaining investor confidence is akin to nurturing a delicate plant. India recognizes the importance of transparent communication and accountability in public debt management. Regular disclosures, clear fiscal targets, and adherence to sound financial principles help build trust among investors and citizens alike.
Global Economic Dynamics:
In a world where economic ties transcend borders, India’s public debt management isn’t isolated. Global economic dynamics, changes in interest rates, and shifts in investor sentiments all play a role. Flexibility and adaptability in response to these external factors are integral to India’s approach.
Conclusion:
Public debt management in India is a dynamic and intricate field, where every move impacts the nation’s economic condition. As the country strides towards progress, the challenge lies not only in managing debts but in leveraging them wisely for sustainable growth. With a judicious mix of financial instruments, strategic planning, and a commitment to fiscal responsibility, India navigates the complex seas of public debt management, ensuring that the economic ship sails towards a resilient and prosperous future.