Vision and Strategy for India’s Twelfth Plan
India, a diverse and vibrant nation, is at the cusp of its 12th Five Year Plan, a crucial period that lays the foundation for progress and development. In this blog post, we delve into the vision and strategy that will shape the trajectory of India’s growth over the next five years.
The broad vision and aspirations which the Twelfth Plan sought to fulfil are reflected in the subtitle of the Plan itself: Faster, Sustainable and More Inclusive Growth.
Table of Contents
Rapid Growth
As correctly emphasized in the 12th Five Year Plan document, while the objective of development is broad-based improvement in the economic and social conditions of our people, rapid growth of GDP is an essential requirement for achieving this objective. The target for GDP growth in the Twelfth Plan was kept at 8.0 per cent per annum.

Inclusiveness
The Plan emphasised the following dimensions of inclusiveness:
Inclusiveness as poverty reduction:
Distributional concerns have traditionally been viewed as ensuring an adequate flow of benefits to the poor and the most marginalised.
Inclusiveness as group equality:
While poor are certainly one target, inclusiveness must also embrace the concern of other groups such as the scheduled castes, scheduled tribes, other backward classes, minorities, the differently abled and marginalised groups.
Inclusiveness as regional balance:
Another aspect of inclusiveness relates to whether all States, and indeed all regions, are seen to benefit from the growth process.
Inclusiveness and inequality:
Inclusiveness also means greater attention to income inequality.
Inclusiveness as empowerment:
Finally, inclusiveness is not just about ensuring a broad-based flow of benefits or economic opportunities, it is also about empowerment and participation.
Environmental Sustainability:
With increasing levels of environmental pollution around the world and the threat of climate change caused by the accumulation of carbon dioxide and other Greenhouse Gases (GHG) in the atmosphere due to human activity, the issue of environmental sustainability has emerged as a crucial one.
Monitorable Targets for the 12th Five Year Plan:
The Twelfth Plan identified 25 core indicators divided into seven categories: (1.) Economic growth, (2.) Poverty and employment, (3.) Education, (4.) Health, (5.) Infrastructure, including rural infrastructure, (6.) Environment and sustainability, and (7.) Service delivery.
Vision: A Prosperous and Inclusive India
At the core of the 12th five year Plan is the vision of a prosperous and inclusive India, where the benefits of development reach every corner of society. The aim is not just economic growth but growth that uplifts the lives of the common citizen, fostering a sense of unity and shared progress.
1. Economic Growth with Social Inclusion
The plan envisages a balanced approach to economic growth, emphasizing the need for inclusive policies that bridge the gap between the affluent and the marginalized. By focusing on sectors that generate employment and empower local communities, the plan aims to create a more equitable distribution of wealth.

2. Sustainable Development
With environmental concerns looming large, the 12th five year Plan places a significant emphasis on sustainable development. Striking a balance between economic growth and environmental conservation, the vision is to build a future where progress is harmonized with nature, ensuring a greener and healthier India.
Strategy: Building Blocks for a Resilient Future
The success of any plan lies in its execution, and the 12th five year Plan adopts a comprehensive strategy that addresses key areas crucial for the nation’s progress.
1. Infrastructure Development
A robust infrastructure is the backbone of any growing economy. The plan outlines extensive investments in infrastructure projects, including roads, railways, and digital connectivity. This not only accelerates economic activities but also enhances the overall quality of life for citizens.
2. Skill Development and Education
Empowering the youth with skills that are relevant to the evolving job market is a key focus. The 12th Five Year Plan aims to revamp the education system, aligning it with the demands of the industry. By investing in skill development programs, the plan seeks to create a workforce that can meet the challenges of the 21st century.
3. Healthcare for All
The ongoing global health crisis has underscored the importance of a robust healthcare system. The 12th Five Year Plan recognizes this and places healthcare at the forefront. Initiatives for building and upgrading medical infrastructure, along with policies that ensure universal access to quality healthcare, are pivotal components of the strategy.
4. Digital Transformation
In the age of technology, digital transformation is not just an option but a necessity. The plan envisions a digitally empowered India, leveraging technology to streamline governance, enhance efficiency, and bridge the urban-rural divide. The aim is to create a connected nation where the benefits of the digital revolution reach every citizen.
5. Social Welfare Programs
Ensuring social justice and upliftment of marginalized communities is integral to the 12th Five Year Plan. The strategy includes targeted social welfare programs that address issues of poverty, gender inequality, and social discrimination. By creating a more inclusive society, the plan aims to unlock the full potential of every citizen.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the vision and strategy of the 12th Five Year Plan set an ambitious course for India’s future, challenges abound. From global economic uncertainties to internal complexities, navigating the path to progress requires resilience and adaptability. However, within challenges lie opportunities, and the plan recognizes the potential for innovation and growth in emerging sectors.
Conclusion: A Shared Journey Towards Progress
As India embarks on the 12th Five Year Plan, it is not just a governmental initiative but a collective journey involving every citizen. The vision and strategy outlined are a roadmap, and their success hinges on the active participation and commitment of the people. Through unity, perseverance, and a shared vision of progress, India aims to build a future that is not only economically robust but socially inclusive and environmentally sustainable. The 12th Five Year Plan is a call to action, inviting every Indian to contribute to the nation’s growth and prosperity. Together, we can turn this vision into reality, ensuring a brighter and more promising tomorrow for generations to come.
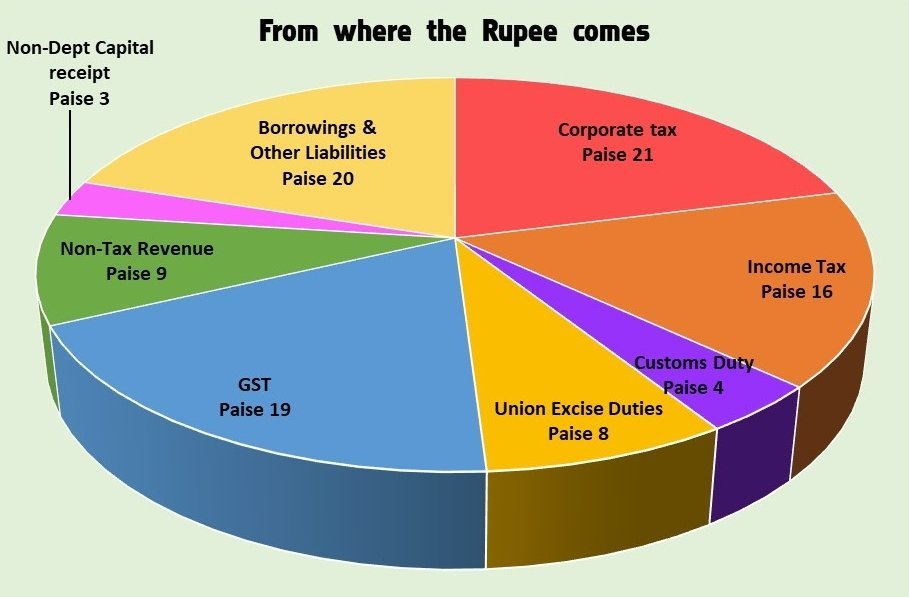
India’s Economic Landscape: Unpacking the Twelfth Plan’s Macroeconomic Framework and Financing Patterns
As we delve into the intricate tapestry of India’s economic roadmap, the 12th Five Year Plan emerges as a crucial chapter in the nation’s development narrative. This plan, spanning from 2012 to 2017, set the stage for a holistic approach to economic growth, emphasizing inclusive development and sustainability.
Macroeconomic Framework: The Blueprint for Growth
At the heart of the 12th Five Year Plan lies a robust macroeconomic framework, a blueprint meticulously designed to steer India towards prosperity. One of the key pillars was achieving a balanced growth trajectory, encompassing various sectors and demographics. This meant not just focusing on the urban elite but also addressing the needs of the rural population.
The plan underscored the importance of infrastructure development as a catalyst for economic growth. Investments in sectors like transportation, energy, and telecommunications were prioritized to create a solid foundation for sustainable development. This approach recognized that a well-connected and energy-efficient nation is better equipped to leverage its economic potential.
Additionally, the 12th Five Year Plan recognized the significance of social sectors such as education and healthcare. A skilled and healthy population is an asset for any nation aspiring to thrive in the global arena. By allocating resources to these areas, the plan aimed to empower citizens and enhance their contribution to the economy.
Financing Patterns: Navigating the Fiscal Landscape
Executing such an ambitious plan required a thoughtful financing strategy. The 12th Five Year Plan adopted a multi-pronged approach, leveraging both public and private resources. Government expenditure played a pivotal role, with increased allocations to key sectors. Simultaneously, the plan encouraged private sector participation through public-private partnerships (PPPs), fostering collaboration for infrastructure development.
Moreover, the plan emphasized the need for fiscal consolidation, aiming to strike a balance between stimulating economic growth and maintaining fiscal discipline. This involved measures to enhance revenue generation and rationalize expenditures. The goal was to create a sustainable fiscal environment that could weather economic uncertainties.
In tandem with fiscal consolidation, the 12th Five Year Plan recognized the importance of monetary policy in shaping the economic landscape. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) played a crucial role in maintaining price stability and ensuring a conducive environment for investment. Interest rate adjustments and liquidity management were employed as tools to fine-tune the economy.
Challenges and Achievements: Navigating the Economic Terrain
While the 12th Five Year Plan laid out an ambitious roadmap, it encountered its share of challenges. The global economic landscape, marked by uncertainties and fluctuations, posed external challenges that necessitated agile policy responses. Domestically, issues such as inflation and a widening fiscal deficit required careful navigation.
However, amidst these challenges, the 12th Five Year Plan recorded significant achievements. The focus on inclusive growth led to poverty reduction, and social indicators such as literacy and life expectancy showed improvement. Infrastructure projects, supported by both public and private investments, contributed to enhanced connectivity and efficiency.

Looking Ahead: Lessons for the Future
As we reflect on the 12th Five Year Plan’s macroeconomic framework and financing patterns, there are valuable lessons to carry forward. The emphasis on balanced growth, infrastructure development, and inclusive policies remains relevant. The need for a prudent fiscal strategy and the importance of adapting to global economic dynamics are timeless principles.
In the context of India’s subsequent economic plans, building upon the successes and learning from the challenges of the Twelfth Plan is imperative. The evolving global landscape and the rise of new challenges underscore the importance of agility and adaptability in economic policymaking.
In conclusion, the 12th Five Year Plan serves as a significant chapter in India’s economic saga. Its macroeconomic framework and financing patterns reflect a thoughtful approach to fostering sustainable and inclusive growth. As India continues its journey, the lessons from the 12th Five Year Plan provide a compass for navigating the complexities of the economic terrain.
Sectoral Challenges: Insights into India’s 12th Five Year Plan
As we rewind the economic tapestry of India’s 12th Five Year Plan (2012-2017), it becomes evident that the journey to progress was not without its sectoral hurdles. This pivotal period witnessed a concerted effort to address and overcome challenges across various sectors, each playing a unique role in shaping the nation’s growth trajectory.
1. Agriculture: Cultivating Resilience
The agricultural sector, often hailed as the backbone of India, faced multifaceted challenges during the 12th Five Year Plan. Erratic weather patterns, insufficient irrigation facilities, and the need for technology adoption were among the hurdles. The plan recognized the importance of modernizing agriculture, with a focus on sustainable practices and increased investment in rural infrastructure. Despite progress, the agricultural sector continued to grapple with the need for comprehensive reforms to ensure the well-being of farmers and food security for the nation.
2. Manufacturing: Navigating Industrial Waters
The 12th Five Year Plan aimed to boost the manufacturing sector, envisioning it as a key driver of economic growth and employment generation. However, the sector faced issues like regulatory bottlenecks, complex tax structures, and the need for skill development. Efforts were made to simplify regulatory frameworks and encourage innovation. While strides were made, addressing the structural impediments to manufacturing growth remained an ongoing challenge.
3. Infrastructure: Paving the Path Forward
Infrastructure development was a linchpin in the 12th Five Year Plan’s growth strategy. Despite concerted efforts, challenges such as project delays, funding gaps, and the need for streamlined approvals persisted. The plan acknowledged the need for a conducive environment to attract private investments in infrastructure projects. Overcoming bureaucratic hurdles and ensuring timely implementation remained critical to realizing the full potential of infrastructure as an engine of economic growth.
4. Health and Education: Nurturing Human Capital
The 12th Five Year Plan recognized the pivotal role of health and education in fostering inclusive growth. However, the sectors faced challenges like unequal access, quality disparities, and the need for innovative solutions. The plan prioritized improving healthcare infrastructure, enhancing educational outcomes, and promoting skill development. Yet, the journey towards achieving equitable access to quality healthcare and education for all remained a work in progress.

5. Energy: Powering Progress Responsibly
The energy sector grappled with the dual challenge of meeting growing demands while transitioning towards sustainable practices. Issues such as fuel pricing, energy security, and environmental concerns were at the forefront. The 12th Five Year Plan endeavored to strike a balance by promoting renewable energy sources and encouraging energy efficiency. However, the transition to cleaner energy pathways posed economic and logistical challenges that required sustained efforts beyond the plan period.
6. Financial Inclusion: Bridging Economic Divide
Addressing economic disparities and ensuring financial inclusion were key components of the 12th Five Year Plan. The challenges included reaching the unbanked population, promoting digital transactions, and ensuring the effectiveness of social welfare programs. The plan emphasized the importance of inclusive financial policies but acknowledged the need for continued innovation to make these initiatives more impactful on the ground.
In retrospect, the 12th Five Year Plan in India grappled with diverse sectoral challenges, each requiring a tailored approach for resolution. While significant strides were made, the journey towards overcoming these hurdles is an ongoing one. The lessons learned during this period continue to inform subsequent economic strategies, emphasizing the need for adaptability and persistence in the pursuit of a more resilient and inclusive India.