Objectives of Fiscal Policy
Introduction :
In the intricate dance of economic governance, fiscal policy emerges as a key choreographer, orchestrating the movements of government revenue and expenditure to foster a robust and balanced economy. India, with its diverse and dynamic economic landscape, employs fiscal policy as a powerful tool to achieve various objectives that go beyond mere numbers on a budget sheet. Let’s delve into the human-friendly realm of understanding the objectives of fiscal policy in India.
Table of Contents
Economic Growth and Stability
At the heart of fiscal policy lies the aspiration for economic growth and stability. By strategically managing government spending and taxation, authorities aim to create an environment conducive to sustained economic expansion. The idea is to strike a balance that fuels growth without compromising the stability of the overall economic structure. In India, where the economy is a kaleidoscope of sectors, this objective becomes paramount for ensuring prosperity reaches every corner.
Employment Generation
Fiscal policy in India isn’t just about balancing the books; it’s about putting people to work. The government seeks to create job opportunities by directing fiscal measures toward sectors with high employment potential. Whether through infrastructure projects, skill development programs, or incentives for labor-intensive industries, the goal is to reduce unemployment and underemployment, weaving a stronger social fabric.
Price Stability and Inflation Control
The cost of living is a tangible concern for every citizen. Fiscal policy steps into the fray to tackle inflation and maintain price stability. By fine-tuning expenditure and managing the money supply, the government aims to keep inflation at bay, ensuring that the purchasing power of the common man remains resilient. This objective is crucial for fostering an environment where citizens can plan their financial future without being blindsided by erratic price movements.
Redistribution of Income and Wealth
India’s economic tapestry is woven with threads of diversity, but it also bears the stains of income inequality. Fiscal policy endeavors to bridge this gap by implementing measures that redistribute income and wealth more equitably. Progressive taxation, social welfare programs, and targeted subsidies are tools in this arsenal, seeking to uplift the less privileged sections of society and build a more inclusive economic order.
Promotion of Sustainable Development
In an era where environmental concerns echo globally, fiscal policy in India extends its reach to promote sustainable development. Incentives for green technologies, eco-friendly practices, and responsible resource management reflect the commitment to balance economic progress with environmental stewardship. The goal is not just growth for the present generation but a legacy that future generations can inherit without compromise.
External Stability and Balance of Payments
In an interconnected world, fiscal policy in India isn’t confined to domestic boundaries. It also sets its sights on maintaining external stability and a favorable balance of payments. Through strategic management of trade policies, foreign exchange reserves, and capital flows, the government aims to shield the economy from external shocks and ensure a steady integration into the global economic arena.
Infrastructure Development
Building the foundation for a robust and modern economy requires investing in infrastructure. Fiscal policy channels resources into projects that enhance transportation, communication, energy, and other critical sectors. This not only boosts economic productivity but also lays the groundwork for a better quality of life for citizens across urban and rural landscapes.
Financial Market Stability
The stability of financial markets is vital for a healthy economy. Fiscal policy in India plays a role in regulating and strengthening financial institutions, ensuring that the markets operate efficiently and transparently. This objective safeguards against systemic risks and fosters confidence among investors, both domestic and international.
As we navigate the labyrinth of fiscal policy objectives in India, it becomes clear that behind the numbers and budgetary allocations are human aspirations for a better life, stable employment, and a fair distribution of opportunities. Fiscal policy, in its nuanced dance, strives to harmonize these aspirations, creating a symphony of economic progress that resonates across the diverse and vibrant landscape of India.
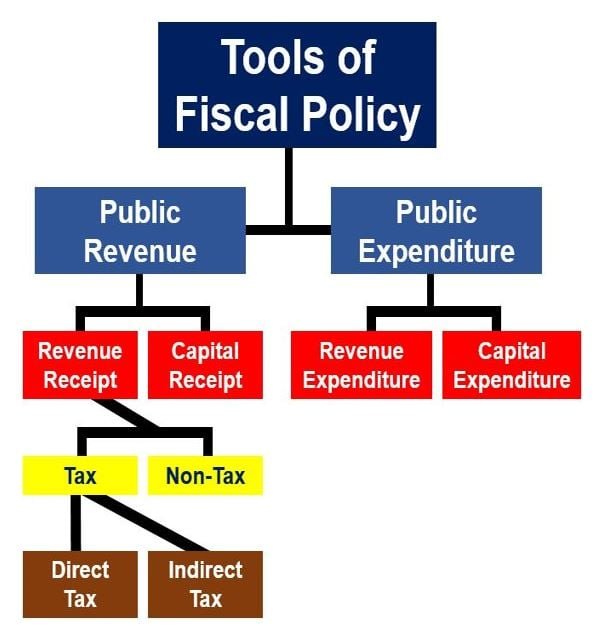
Understanding Fiscal Imbalance and Deficit Finance in India
In the intricate tapestry of India’s economic landscape, the terms “fiscal imbalance” and “deficit finance” often take center stage, playing crucial roles in the nation’s financial narrative. But what do these terms really mean, and how do they impact the lives of ordinary citizens? Let’s embark on a journey to demystify the complexities of fiscal imbalance and deficit finance in India, translating economic jargon into a language we can all understand.
Fiscal Imbalance: Navigating the Economic Tightrope
At its core, fiscal imbalance refers to the misalignment between a government’s revenue and expenditure. It’s like trying to balance a seesaw—when one side (expenditure) is significantly heavier than the other (revenue), the seesaw tilts, and problems arise. In India, achieving a perfect balance is a perpetual challenge due to the diverse demands on the government’s purse strings.
Revenue Collection Challenges
Imagine trying to fill a leaky bucket; that’s often the scenario when it comes to revenue collection in India. Despite efforts to broaden the tax base, the government faces hurdles like tax evasion and an informal economy, making it challenging to collect the funds needed to meet its expenditures. Fiscal imbalance creeps in when the revenue falls short of the government’s financial commitments.
Expenditure Pressures
On the other side of the seesaw, we have government expenditures—essential for running the nation. From building infrastructure to funding social welfare programs, the government juggles numerous responsibilities. However, when the expenditure scale tips disproportionately, it leads to fiscal imbalance. Striking the right balance becomes an intricate dance, ensuring the government fulfills its duties without overburdening its financial capacity.
Deficit Finance: Bridging the Financial Gap
Enter deficit finance, the pragmatic response to fiscal imbalance. When expenditures outstrip revenues, a budget deficit emerges. Deficit finance steps in as the government’s strategy to bridge this financial gap, borrowing funds to meet its obligations. Think of it as taking a loan to cover monthly expenses when your paycheck falls short.
Types of Deficits
There are various shades to deficit finance, each revealing a unique facet of the economic landscape:
Revenue Deficit: This occurs when the government’s current revenue falls short of covering its current expenditure. It implies that a chunk of the day-to-day expenses is being met through borrowed funds.
Fiscal Deficit: A broader measure, fiscal deficit includes not only the revenue shortfall but also the borrowings needed to meet capital expenditures. It gives a comprehensive picture of the government’s overall financial health.
Primary Deficit: This is the fiscal deficit minus interest payments. It provides insights into the government’s ability to meet its non-interest obligations from its revenue.
Impact on Economy and Citizens
While deficit finance can be a necessary tool, it’s not without consequences. On the positive side, it enables the government to continue essential spending even during revenue shortfalls. However, excessive reliance on deficit finance can lead to inflation, increased public debt, and potential long-term economic instability. These repercussions have a ripple effect, influencing everything from the cost of goods and services to the interest rates on loans that citizens rely on.
The Indian Context: Balancing Act Amid Diversity
India’s fiscal story is as diverse as its cultural tapestry. Multiple factors contribute to the perpetual tightrope walk of fiscal imbalance and deficit finance:
Social Welfare Commitments
India’s commitment to inclusive growth manifests in extensive social welfare programs. From subsidized food to employment guarantees, these initiatives place a significant burden on government finances. Fiscal imbalance becomes pronounced as the government grapples with balancing these noble commitments against the need for financial prudence.
Infrastructure Imperatives
The call for modern infrastructure echoes across India’s vast landscape. Building roads, bridges, and smart cities demands substantial investment. While these endeavors contribute to long-term economic growth, they also tip the scales, pushing the government towards deficit financing.
Global Economic Realities
In an interconnected world, India is not immune to global economic shifts. External factors, such as fluctuations in oil prices or disruptions in international trade, can exert additional pressure on the nation’s fiscal health. Balancing these external shocks adds an extra layer of complexity to the economic puzzle.
Striking a Balance: The Way Forward
As we navigate the intricacies of fiscal imbalance and deficit finance in India, the key lies in striking a delicate balance. The government must walk the tightrope, ensuring that essential expenditures are met without compromising long-term economic stability. This journey involves:

Efficient Revenue Management:
Plugging leaks in revenue collection, curbing tax evasion, and promoting a transparent tax system are crucial steps to enhance the government’s financial capacity.
Prudent Expenditure Planning:
Prioritizing expenditures, focusing on productive investments, and optimizing resource allocation are essential for a sustainable fiscal framework.
Investment in Productivity:
Channeling borrowed funds into projects that enhance productivity and contribute to economic growth can offset the potential negative impacts of deficit finance.
Global Collaboration:
In an interconnected world, collaborating with the international community to navigate global economic challenges ensures a more resilient fiscal strategy.
Conclusion: A Balancing Act for All
As we unravel the mysteries of fiscal imbalance and deficit finance in India, it’s clear that this financial balancing act isn’t confined to policymakers and economists alone. Every citizen plays a part in this narrative, as the consequences of fiscal decisions reverberate through our daily lives. By understanding the delicate dance between revenue and expenditure, we empower ourselves to actively engage in shaping an economic future that benefits us all. Balancing the ledger becomes a collective endeavor, where fiscal responsibility and economic prudence pave the way for a brighter tomorrow.