India’s Economic Landscape: The Significance of Export and Import in the Planning Period
In the intricate tapestry of India’s economic development, the dynamics of export and import play a pivotal role. As we delve into the nuances of the planning period, it becomes evident that these two facets are not just numbers on balance sheets; they are the lifeblood of a thriving economy.
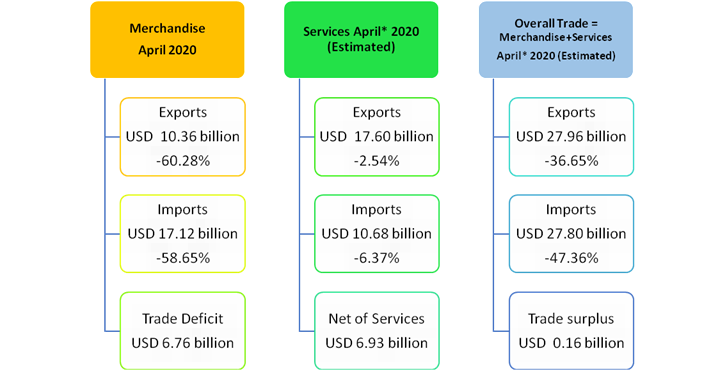
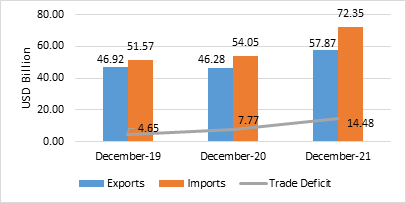
In fact, a study of foreign trade data reveals that trade balance was positive in only two years during the entire period 1949-50 to till now. These were the years of 1972-73 and 1976-77 when the country recorded small trade surpluses of $134 million and $ 77 million respectively. In all other years, deficits in balance of trade were recorded.
Table of Contents
Setting the Stage: Understanding the Planning Period
The planning period in India is a crucial chapter in its economic history, marked by strategic initiatives and foresighted policies aimed at sustainable growth. As the nation charts its course, the value of export and import becomes a compass guiding the trajectory of economic prosperity.
Export-Led Growth: A Catalyst for Development
Exporting goods and services isn’t merely a transaction; it’s a powerful engine that propels economic growth. During the planning period, India strategically harnessed the potential of export-led growth to diversify its revenue streams and establish a global footprint.
1. Economic Diversification
Exporting allows India to tap into diverse markets, reducing dependence on a single sector. The planning period witnessed a deliberate effort to diversify exports, ensuring resilience against economic uncertainties.
2. Job Creation
A surge in export-oriented industries translates into increased employment opportunities. From manufacturing hubs to technology parks, the planning period focused on nurturing sectors with export potential, fostering job creation across the nation.
3. Foreign Exchange Reserves
Healthy exports contribute to robust foreign exchange reserves. This financial cushion not only stabilizes the economy but also empowers the nation to weather economic storms, ensuring a steady flow of resources for development projects.
Import Dynamics: Balancing Act for Sustainable Growth
While export-led growth is a cornerstone, the judicious management of imports is equally vital. The planning period sought to strike a delicate balance, recognizing the importance of imports in fostering innovation and maintaining competitiveness.
1. Technological Advancements
Imports often bring in cutting-edge technologies that propel industries forward. The planning period witnessed strategic imports, especially in the fields of science and technology, fostering innovation and enhancing India’s global competitiveness.
2. Raw Materials and Resources
To fuel its ambitious growth plans, India looked beyond borders for essential raw materials. Access to quality imports ensured a seamless supply chain, preventing bottlenecks in manufacturing processes and supporting the production of high-quality goods.
3. Consumer Goods and Cultural Exchange
Imported goods aren’t just commodities; they represent a bridge connecting cultures. The planning period acknowledged the significance of importing consumer goods, facilitating a cultural exchange that goes beyond economic transactions.
Challenges and Solutions
Navigating the intricate web of export and import isn’t without challenges. The planning period witnessed hurdles such as trade imbalances, fluctuating currency values, and global economic uncertainties. However, India responded with resilience and adaptability, implementing measures to mitigate risks and seize opportunities.
1. Trade Agreements and Alliances
Strategic trade agreements and alliances became key instruments in fostering mutually beneficial relationships. By aligning with like-minded nations, India expanded its market reach and minimized trade barriers, ensuring smoother export and import processes.
2. Infrastructure Development
A robust infrastructure is the backbone of a flourishing trade ecosystem. The planning period prioritized infrastructure development, from modernizing ports to enhancing transportation networks, streamlining the movement of goods and reducing logistics costs.
Looking Ahead: A Future Anchored in Trade
As India strides into the future, the value of export and import continues to be a linchpin in its economic planning. The lessons learned during the planning period underscore the need for adaptability, foresight, and a proactive approach in navigating the ever-evolving global economic landscape.
In conclusion, the planning period in India is a testament to the transformative power of export and import. Beyond the statistical figures, these economic activities are the threads that weave together a narrative of growth, innovation, and resilience. As India continues to carve its destiny, the significance of export and import will remain etched in the annals of its economic history.
Composition of Foreign Trade in the Indian Economy
Foreign trade has long been the lifeblood of economic growth, and in the vibrant tapestry of the Indian economy, it plays a pivotal role. As we delve into the intricate web of global transactions, let’s unravel the composition of foreign trade in India and understand how it shapes the nation’s economic landscape.
Historical Perspective:
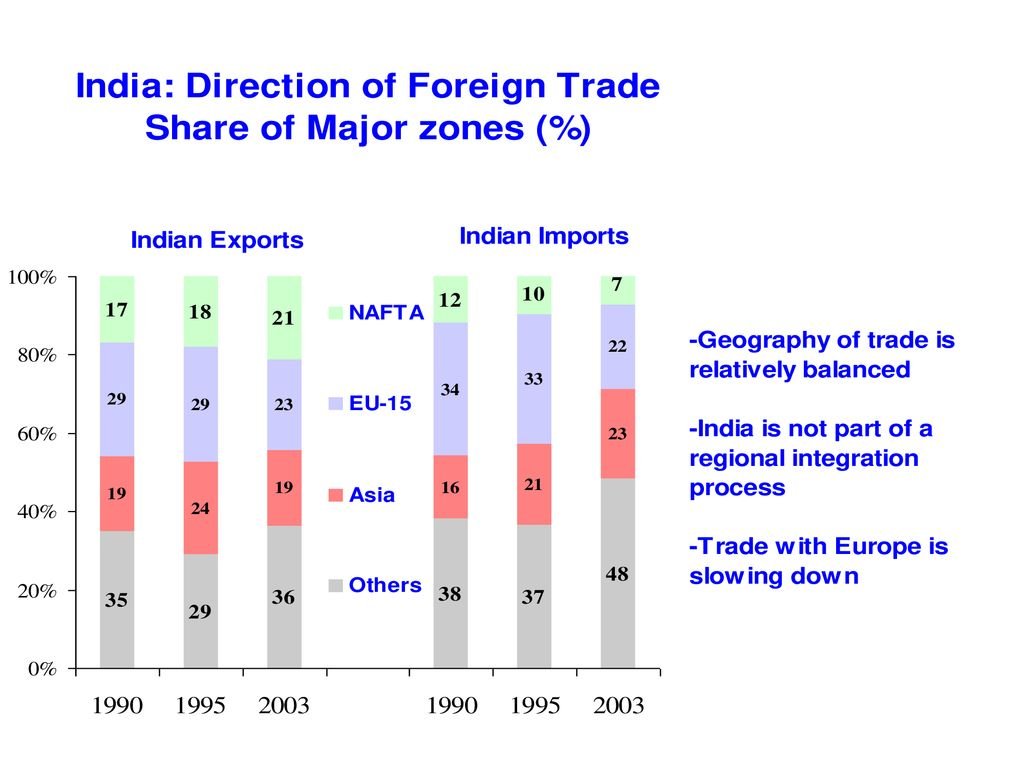
To comprehend the present, we must glance back at the past. India’s engagement in foreign trade dates back centuries, tracing the footsteps of ancient trade routes. The historical Silk Road and maritime trade shaped the country’s economic identity, fostering a rich tapestry of cultural exchange.
Evolution of Trade Policies:
The post-independence era witnessed a shift from protectionism to liberalization. The 1991 economic reforms marked a turning point, opening doors to globalization. Trade policies evolved, paving the way for increased foreign direct investment (FDI) and trade partnerships.
Exports and Imports:
India’s foreign trade is a two-way street, comprising both exports and imports. Exports showcase the nation’s strengths, ranging from textiles and IT services to pharmaceuticals and automotive components. Meanwhile, imports meet domestic demands, encompassing crude oil, machinery, electronics, and more.
Bilateral and Multilateral Trade Agreements:
In the interconnected world, bilateral and multilateral trade agreements shape the dynamics. India actively engages in negotiations, fostering partnerships with countries across the globe. Agreements like ASEAN, SAFTA, and FTAs contribute to a complex yet dynamic network of trade relationships.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Every trade journey encounters hurdles, and India is no exception. From trade imbalances to geopolitical tensions, challenges persist. However, these challenges also present opportunities for growth and innovation, encouraging the nation to diversify its trade portfolio.
Role of Technology:
In the 21st century, technology acts as a catalyst, transforming the landscape of foreign trade. E-commerce platforms bridge gaps, enabling small and medium enterprises to participate in global markets. Digitalization enhances transparency and efficiency, redefining the contours of international trade.
Impact on the Economy:
The composition of foreign trade significantly influences the overall economic health of the nation. A robust export sector contributes to GDP growth, employment generation, and technological advancements. Conversely, import dependencies pose challenges, necessitating strategic planning for a balanced trade ecosystem.
Sustainable Trade Practices:
As the world grapples with environmental concerns, sustainable trade practices come to the forefront. India, recognizing the importance of eco-friendly trade, is embracing green initiatives. From renewable energy exports to sustainable agriculture practices, the nation aims to create a trade landscape aligned with global sustainability goals.
Future Trajectory:
The future of Indian foreign trade promises continued evolution. With a growing emphasis on innovation, diversification, and sustainability, India envisions a role as a key player in the global economic arena. Investments in research and development, coupled with strategic trade partnerships, will shape the trajectory ahead.
Conclusion:
In the intricate mosaic of the Indian economy, foreign trade is a vibrant thread that weaves through history, policy evolution, challenges, and opportunities. As the nation continues to navigate the global marketplace, understanding the composition of foreign trade becomes crucial for fostering economic resilience, growth, and a harmonious coexistence in the global community.